Have you ever seen that your computer starts booting slowly? Or it slowly restores its state from hibernation. Maybe you observe performance issues when shutdown or hibernate process? In this article, I will show you how you can use Event Log Explorer to find performance problems linked with the startup/shutdown/hibernate/resume processes.
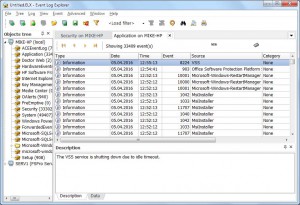
Starting from Windows Vista, Microsoft provides a bunch of event logs for different system purposes. In Windows Event Viewer, these logs are located in a special branch: “Applications and Services Logs”. Windows records performance diagnostics events into Microsoft-Windows-Diagnostics-Performance/Operational event log. To open this log in Windows Event Viewer, open Applications and Services Logs branch, then open Microsoft, then open Windows, then select Diagnostics-Performance and click on Operational. In Event Log Explorer you can do it easier: open your computer in the tree, then open Microsoft-Windows folder and then click Microsoft-Windows-Diagnostics-Performance/Operational.
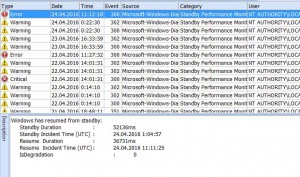
Now you can see a list of different diagnostic events. As you can see, events with the same event ID may have different types – Warning, Error and Critical. It looks like these event types depend on the duration of the startup/shutdown process. Another observation – theses events contain many important parameters internally, but you can’t see them in the event description (Windows Event Viewer doesn’t display them as well). The only way to display these parameters is to double click on the event to display event properties and switch to XML tab.
Unfortunately, I didn’t find a detailed documentation about all these events, so I did some research. First, I got meaning of events in Microsoft-Windows-Diagnostics-Performance:
| Event ID | Event Description |
| Boot Performance Monitoring | |
| 100 | Windows has started up |
| 101 | This application took longer than usual to start up, resulting in a performance degradation in the system startup process |
| 102 | This driver took longer to initialize, resulting in a performance degradation in the system start up process |
| 103 | This startup service took longer than expected to startup, resulting in a performance degradation in the system start up process |
| 104 | Core system took longer to initialize, resulting in a performance degradation in the system start up process |
| 105 | Foreground optimizations (prefetching) took longer to complete, resulting in a performance degradation in the system start up process |
| 106 | Background optimizations (prefetching) took longer to complete, resulting in a performance degradation in the system start up process |
| 107 | Application of machine policy caused a slow down in the system start up process |
| 108 | Application of user policy caused a slow down in the system start up process |
| 109 | This device took longer to initialize, resulting in a performance degradation in the system start up process |
| 110 | Session manager initialization caused a slow down in the startup process |
| Shutdown Performance Monitoring | |
| 200 | Windows has shutdown |
| 201 | This application caused a delay in the system shutdown process |
| 202 | This device caused a delay in the system shutdown process |
| 203 | This service caused a delay in the system shutdown process |
| Standby Performance Monitoring | |
| 300 | Windows has resumed from standby |
| 301 | This application caused a delay during standby |
| 302 | This driver caused a delay during standby while servicing a device |
| 303 | This service caused a delay during hybrid-sleep |
| 304 | Creation of the hiber-file was slower than expected |
| 305 | Persisting disk caches was slower than expected |
| 306 | Preparing the video subsystem for sleep was slower than expected |
| 307 | Preparing Winlogon for sleep was slower than expected |
| 308 | Preparing system memory for sleep was slower than expected |
| 309 | Preparing core system for sleep was slower than expected |
| 310 | Preparing system worker threads for sleep was slower than expected |
| 350 | Bios initialization time was greater than 250ms (logo requirement) during system resume |
| 351 | This driver responded slower than expected to the resume request while servicing this device |
| 352 | Reading the hiber-file was slower than expected |
| System Performance Monitoring | |
| 400 | Information about the system performance monitoring event |
| 401 | This process is using up processor time and is impacting the performance of Windows |
| 402 | This process is doing excessive disk activities and is impacting the performance of Windows |
| 403 | This driver is using up too many resources and is impacting the performance of Windows |
| 404 | This driver is waiting longer than expected on a device |
| 405 | This file is fragmented and is impacting the performance of Windows |
| 406 | Disk IO to this file is taking longer than expected |
| 407 | This process is using up too much system memory |
| 408 | Many processes are using too much system memory |
| Desktop Window Manager Monitoring | |
| 500 | The Desktop Window Manager is experiencing heavy resource contention |
| 501 | The Desktop Window Manager is experiencing heavy resource contention |
Since we research boot/shutdown/standby/resume performance, we should pay attention to 1xx, 2xx and 3xx events. We can see that events 100, 200 and 300 are basic events followed by 1xx, 2xx and 3xx which give extra information about the problem.
E.g. I can see two events
Event 100 : Windows has started up: Boot Duration : 34857ms IsDegradation : 0 Incident Time (UTC) : 18.11.2015 23:58:10
Event 102: This driver took longer to initialize, resulting in a performance degradation in the system start up process: File Name : mssmbios Friendly Name : System Management BIOS Driver Version : 6.1.7600.16385 (win7_rtm.090713-1255) Total Time : 1027ms Degradation Time : 1026ms Incident Time (UTC) : 18.11.2015 23:58:10
So we can see that System Management BIOS Driver caused the delay in the system boot up.
Unfortunately sometimes events 100, 200 and 300 occur alone without followed events. In this case it is impossible to detect the reason of the delay using Diagnostics-Performance event log.
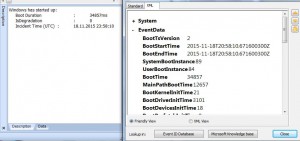
You should pay attention to parameters of Event 100 (Microsoft-Windows-Diagnostics-Performance):
System ... EventData BootTsVersion 2 BootStartTime 2015-11-18T20:58:10.671600300Z BootEndTime 2015-11-18T20:58:10.671600300Z SystemBootInstance 89 UserBootInstance 84 BootTime 34857 MainPathBootTime 12657 BootKernelInitTime 21 BootDriverInitTime 3101 BootDevicesInitTime 18 BootPrefetchInitTime 0 BootPrefetchBytes 0 BootAutoChkTime 0 BootSmssInitTime 5084 BootCriticalServicesInitTime 436 BootUserProfileProcessingTime 2683 BootMachineProfileProcessingTime 0 BootExplorerInitTime 848 BootNumStartupApps 24 BootPostBootTime 22200 BootIsRebootAfterInstall false BootRootCauseStepImprovementBits 0 BootRootCauseGradualImprovementBits 0 BootRootCauseStepDegradationBits 4 BootRootCauseGradualDegradationBits 0 BootIsDegradation False BootIsStepDegradation false BootIsGradualDegradation false BootImprovementDelta 0 BootDegradationDelta 0 BootIsRootCauseIdentified true OSLoaderDuration 735 BootPNPInitStartTimeMS 21 BootPNPInitDuration 1342 OtherKernelInitDuration 332 SystemPNPInitStartTimeMS 1665 SystemPNPInitDuration 1776 SessionInitStartTimeMS 3451 Session0InitDuration 2088 Session1InitDuration 339 SessionInitOtherDuration 2656 WinLogonStartTimeMS 8536 OtherLogonInitActivityDuration 587 UserLogonWaitDuration 3551
Most of parameters are self-descriptive.
Pay attention that BootTime= MainPathBootTime + BootPostBootTime
MainPathBootTime is the time (in milliseconds) from when the Windows Logo first appears on screen and until your desktop or logon prompt is presented.
BootPostBootTime is the time (in milliseconds) from the logon screen or desktop showing up and until the system become actually usable (the system has reached 80% idle).
In many cases (but not in my sample), the problem with long boot time is linked with Windows Prefetcher – you will see that BootPrefetchInitTime is set to a large value, e.g. 60000 or more. In this case you can play with Superfetch service and Superfetch caching parameters (registry key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Memory Management\PrefetchParameters). If you have just changed your HDD or SSD, you should re-run the assessment in Performance Information and Tools applet (or just run Winsat command as winsat.exe diskformal) to make Windows use the best prefetch strategy.
Now you have some background information about Diagnostics-Performance events. In the next part I will show how Event Log Explorer helps to detect boot performance issues.